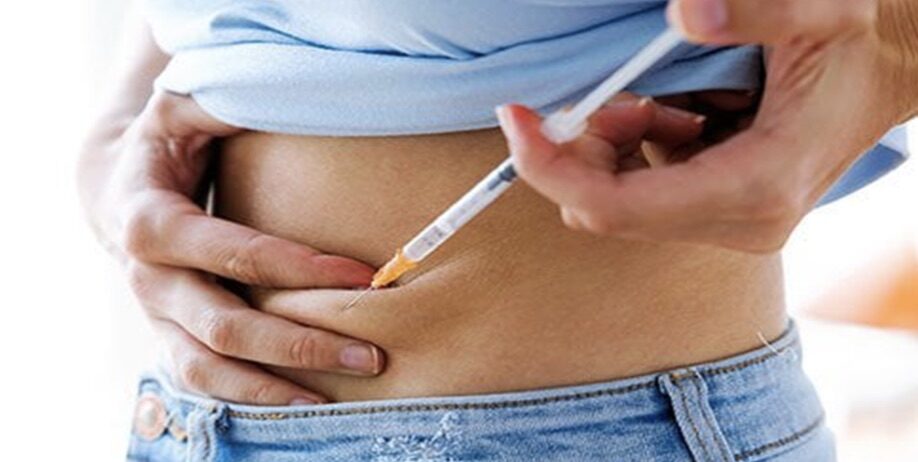
One way to administer medication is through subcutaneous injection. A short needle is used in this method of drug administration to inject the medication into the tissue that lies between the skin and the muscle. As drugs used orally typically take longer to be absorbed than those administered intravenously, this kind of injection is employed when alternative delivery systems for the medication might not be suitable or efficient. CRC Health Centre will make subcutaneous injections commonplace for everyone.
What is a Subcutaneous Injection?
Injections into the layer of fat between the skin and muscles are referred to as subcutaneous injections. There are rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting and long-acting insulins; however, usually a shorter hypodermic needle is used. Common uses for subcutaneous injections may include:
– Insulin for diabetes
– Heparin or anticoagulants
– Vaccination
Where is the Insulin Injection Site?
Abdomen
The distance between the two needles is 1-2 cm. The abdominal injection is typically favoured as the fastest insulin absorption occurs in the abdomen, where the subcutaneous fat is dense and can lessen the risk of injection into the muscle layer.
Thigh

The second fastest insulin absorption occurs in the thighs. In order to avoid injecting into the inner or side of the thigh, the skin should be squeezed and care should be taken to prevent injecting into the inner or side of the thigh.
Buttocks
The subcutaneous layer of the buttocks is relatively thick as there is a lot of fat in this area; thus, there is no need to squeeze the skin.
Upper Arm
When is Long-Acting Insulin Suitable?
Long-acting insulin can generally be injected at bedtime or in the morning. Long-acting insulin is a kind of insulin preparation, and its hypoglycemic effect lasts for a long time, generally lasting 24-36 hours, and needs to be administered by subcutaneous injection. Not all diabetic patients are suitable for long-acting insulin. In the most common type 2 diabetes patients, when metformin is used alone or metformin combined with other hypoglycemic drugs, the blood sugar is out of range. Typically long-acting insulin is considered when an individual’s blood sugar rises significantly and dramatically.

How to Master the Injection Method of Insulin?
Determine the dosage form and location of insulin
Before injecting insulin, you must first understand the type of insulin you need to use from your family doctor so that you can choose the appropriate injection site for you. If you are using rapid-acting insulin, it can be injected anywhere. If short-acting insulin is used, the abdomen is preferred because it is absorbed more quickly. If you are using intermediate-acting insulin, long-acting insulin or premixed insulin, the preferred injection sites are subcutaneous in the buttocks and thighs. It is generally recommended that the injection site should be rotated regularly to avoid long-term injection of one site that could result in local induration and fat atrophy which will affect the absorption of insulin. If induration occurs, warm compresses can be used to relieve it.

Prepare for the injection
Before injecting, check the insulin vial to make sure it is the correct type of insulin and there are no lumps or particles. Install the needle of the insulin pen and make sure to remove the air inside. Then use alcohol to disinfect the skin at the injection site. If you are taking premixed insulin, you should mix it in advance and adjust the appropriate dose.
Perform standardized injections

When injecting, pinch the skin at the injection site with the left hand, press and hold the pen at 45 degrees or vertically to insert the needle with the right hand, press the injection button with the thumb of the right hand and slowly advance the liquid medicine. After the injection, the needle should stay under the skin for 10 seconds before you pull out in the direction of the needle.
Do a good job in post-injection treatment and observation
After the injection, put the used needle on the outer needle cap and throw it away as it cannot be reused. You need to observe your own situation after the injection. If you use too much insulin, eat too little or fail to eat on time, you may experience symptoms of hypoglycemia, a condition in which your blood sugar level is lower than the standard range and you can manifested symptoms such as weakness, hunger, vertigo, cold sweat, pale skin and palpitation. Sometimes these symptoms will worse to hemiplegia, ataxia, tachycardia and coma. If you experience any of those symptoms, you need to seek medical treatment and ask the doctor to evaluate how to adjust the subsequent insulin dosage.
Other things to check out for
– Each insulin pen is dedicated to one person and cannot be shared with other people to avoid the risk of blood transmission.
– When the insulin pen is used for injection for the first time, the needle needs to be exhausted and the two units of insulin can be adjusted to push out.
– Insulin pens should not be exposed to the sun and should not be placed in a place with low temperature to prevent insulin deterioration and failure.
– When not in use for a long time, the insulin pen should be kept in a cool and ventilated place; it can be placed in a refrigerated place.
– The insulin pen should be clean and hygienic during use. If there is any dripping liquid after use, it should be wiped clean.
Heparin Injection
An anticoagulant medication called heparin is used to treat or prevent blood clots. It is offered in various strengths and has a commercial formulation that may be applied subcutaneously. Due to its potentially fatal adverse effects, heparin is also regarded as a dangerous medicine, therefore make sure you double-check the dosage before injecting.

Where is the Heparin Injection Site?
Belly
Make sure you are at least 5 cm (2 inches) from your navel. This is the most commonly recommended site for insulin injections because of stable absorption and ease of self-administration. Gently hold the area, making sure you can pinch 1 to 2 inches of skin.
Thigh
While exposing your thigh for an injection,check midway between the knee and hip and slightly to the side. Hold the region gently while ensuring that you can pinch 1 to 2 inches of skin.
Upper Arms
Expose arms to shoulders. A medical expert typically administers subcutaneous vaccines in this location.
How is Heparin Injected?
1. Clean your hands.
2. Select the site and gather your supplies; prepare disinfectant and swabs.
3. Pinch the area of skin with your thumb and point the needle down at 90 degrees; if you do not do so, the air will bounce to the top of the liquid medication. During the injection, pinch your skin tight to prevent it from slipping.
4. After the injection, remove the needle and press the spot for a minute with a cotton swab. You should not rub the injection site to prevent bruising.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following:
– Cannot self-inject
– Bleeding from the injection site for more than 10 minutes
– Injecting the drug into the wrong place
– Injecting more than the prescribed dose
– Allergy symptoms which includes difficulty breathing, hives or rash